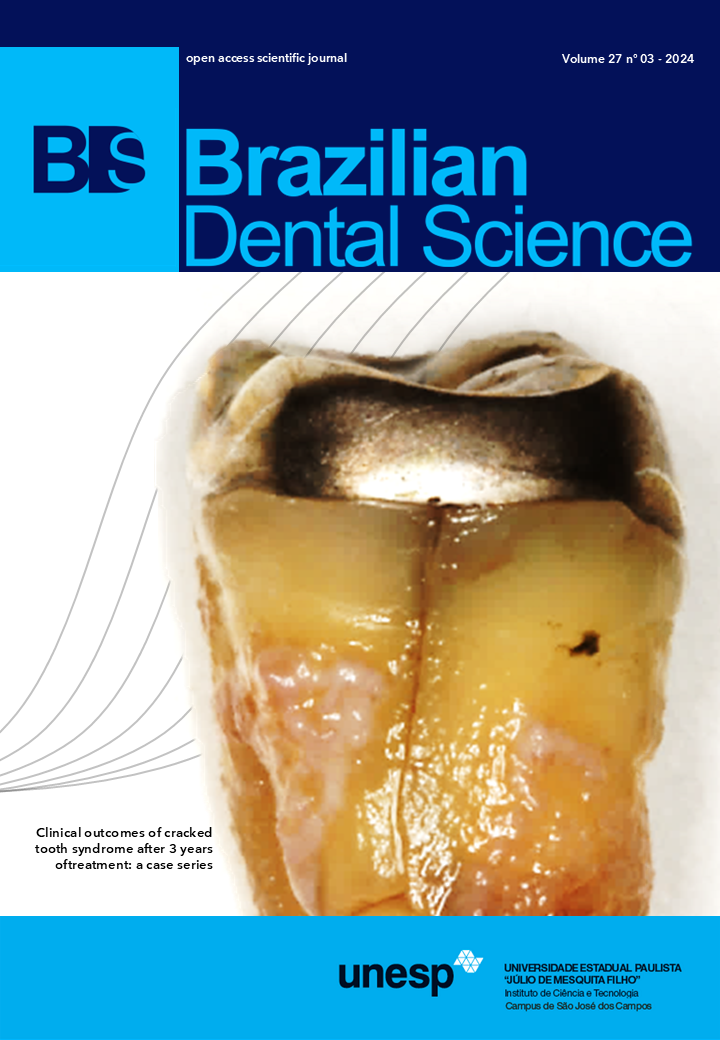
Clinical outcomes of cracked tooth syndrome after 3 years of treatment: a case series
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.4322/bds.2024.e4329Abstract
Background: Diagnosis of cracked tooth syndrome (CTS) requires clinical experience and scientific knowledge. Even providing an effective resolution of the symptoms, clinicians must inform their patients that cracks may progress and induce tooth separation. Thus, follow-up is essential. Case-report: This study describes the treatment of patients with cracked tooth syndrome through a series of three cases. It also includes their long-term followups over three years, through clinical probing and radiography. The findings highlight the importance of periodic check-ups to manage potential complications. Regular follow-ups can help control undesirable responses that may cause pain or make future treatments unfeasible. On all the scenarios presented, an endodontic treatment was needed. On the first successful case the radiolucent lesion regressed with no discomfort or pain. The second case was an unsuccessful one. The patient returned to the dental office after 3 years when probing revealed a 10-mm pocket at the distal aspect of the tooth. The radiography showed distal bone loss. The tooth was extracted to prevent bone loss from progressing. The third report documented the treatment of a patient who declined follow-up care and only returned after 3 years. At that point, a severe mobility was apparent. The radiography revealed a large periapical radiolucency with extensive bone loss, and the tooth extraction became necessary. Conclusion: These cases underscore the importance of informing patients about the potential for crack progression and tooth separation and emphasizes the crucial role of regular follow-up care, as well as discussing the possibilities of restorative treatment.
KEYWORDS
Clinical evolution; Cracked tooth syndrome; Diagnosis, oral; Permanent, dentistry, operative; Tooth crown.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Brazilian Dental Science uses the Creative Commons (CC-BY 4.0) license, thus preserving the integrity of articles in an open access environment. The journal allows the author to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
=================